Gynecomastia
Category: Body
Treatment Details
Session
1
Operation length
1-2 hours
Anesthesia
General
Discomfort Period
1-3 days
Return to work
3-7 days
Full Recovery
3-6 months
Results
Permanent
Hospital Stay
1 Day
An Introduction to Gynecomastia
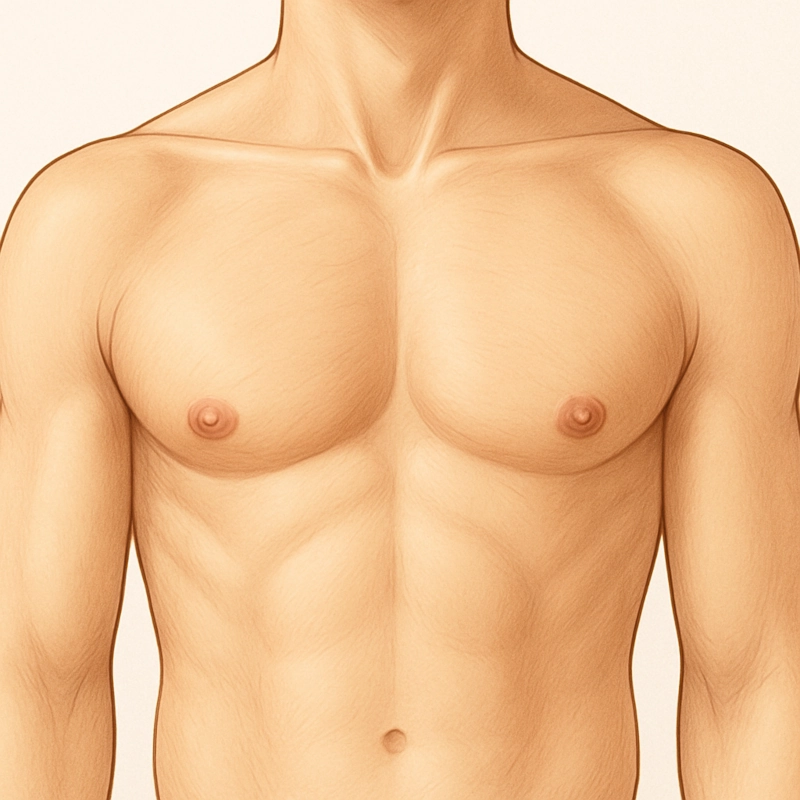
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of glandular breast tissue in boys and men. This growth causes the male breast to enlarge, sometimes resembling a female breast. The primary cause is often an imbalance between the body's normal hormone levels, specifically a relative excess of female hormones (estrogens) compared to male hormones (androgens). While weight gain can contribute to the appearance, true gynecomastia involves the growth of actual breast gland tissue, not just fat.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The signs of gynecomastia can cause both physical and psychological distress. Key symptoms include:
- Swelling and a feeling of tightness in the breast area.
- Tenderness or pain upon touch.
- Physical and emotional discomfort due to the appearance of enlarged breasts.
To diagnose the condition, a doctor will review the patient's history, including any medications or existing diseases, and perform a physical examination of the breast tissue. This exam helps determine the type of gynecomastia and the most suitable treatment. The doctor will assess if the enlargement is caused solely by excess fat tissue (pseudogynecomastia) or if it involves excess glandular breast tissue. It is also crucial to differentiate gynecomastia from male breast cancer. Cancerous lumps are typically unilateral (on one side), feel hard or firm, and can be associated with skin dimpling, nipple retraction or discharge, and enlarged lymph nodes in the underarm area.
What Causes Gynecomastia?
There are dozens of reasons that can lead to male breast growth.
Hormonal Changes Across Life Stages
Gynecomastia can occur at different phases of a male’s life due to natural hormonal fluctuations:
- After Birth: Newborn boys may experience temporary gynecomastia as they are still under the effect of their mother's estrogen. This condition typically resolves within two to three weeks.
- During Puberty: Hormonal shifts during puberty (ages 12-14) are a common cause. In the vast majority of these cases (70-90%), the breast enlargement corrects itself within six months to two years.
- In Mid-life and Beyond: Men between the ages of 50 and 80 are more susceptible to gynecomastia due to age-related hormonal changes.
Underlying Diseases and Health Conditions
Many medical conditions can trigger the development of gynecomastia, including:
- Obesity
- Malnutrition and starvation
- Tumors located in the testicles or adrenal glands
- Liver illness or cirrhosis
- Hyperthyroidism, Hypoandrogenism, or Hypogonadism
- Chronic kidney disease
Medications and Drugs
Gynecomastia can be a side effect of various medications and drugs:
- Steroids: Corticosteroids and anabolic steroids, sometimes used illicitly by athletes to build muscle.
- Heart Medications: Digoxin (Lanoxin) and calcium channel blockers.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications: Such as diazepam (Valium).
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants.
- Antibiotics.
- Ulcer Medications: Such as the over-the-counter drug cimetidine.
- Cancer Treatments.
- Stomach-emptying Medications: Such as metoclopramide (Reglan).
Other Substances
Certain substances are also known to cause gynecomastia:
- Alcohol
- Street drugs such as amphetamines, marijuana, heroin, and methadone.
- Herbal products, particularly plant oils like tea tree or lavender, which may be found in soaps, lotions, or shampoos.
Surgical Treatment for Gynecomastia
Candidates for Surgery
Surgery can be performed on men once puberty is complete, which is typically around 17 years of age. It is not recommended for younger patients before this physiological stage has finished. If a youth is still in puberty, it is best to wait two years to see if the condition resolves on its own.
Surgical Methods
The operation is performed under either general or local anesthetic, depending on the surgeon’s decision and the patient's condition, including age and breast size. The procedure lasts between 1 to 1.5 hours on average. The surgical technique depends on the composition of the breast tissue:
- Glandular Tissue Removal: In cases caused by the growth of the breast gland itself, the excess glandular tissue will be surgically excised.
- Liposuction: In cases caused primarily by excessive fat, liposuction will be used to remove the fat tissue. Liposuction removes fat but not the breast gland itself.
- Combined Approach: Many cases require a combination of both tissue excision and liposuction. In instances where the breasts are excessively large, the surgeon may also need to remove excess skin and tighten the remaining skin for a better contour.
Recovery and Post-Surgery Care
Patients can often leave the medical center on the evening of the operation or the following day. For a smooth recovery:
- You can typically return to normal daily activities the day after the operation.
- Showering or bathing is usually permitted after 2-3 days.
- It is recommended to avoid tight-fitting clothing for the first few months.
- Because the breast gland tissue is removed during the procedure, the regrowth of the breast is generally not possible, making the results permanent.