Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Category: Body
Treatment Details
Session
1
Operation length
1.5-2 hours
Anesthesia
General
Discomfort Period
3-7 Days
Return to work
1-2 Weeks
Full Recovery
1-3 Months
Results
Permanent (with lifestyle change)
Hospital Stay
2 days
What is Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Gastric sleeve surgery is a weight-loss procedure that involves reducing the size of the stomach. The primary goal is to help an individual feel full with significantly less food, leading to substantial weight loss. This surgery is often considered when long-term diet and exercise have not produced successful results, and a person's high body mass index (BMI) is contributing to serious health issues. These can include type 2 diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and various joint or vascular diseases. By surgically reducing the stomach's capacity, the procedure not only aids in weight loss but also helps resolve these associated health problems, leading to improved blood values and overall well-being.
Who is a Candidate for Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
Specific criteria determine who is a suitable candidate for gastric sleeve surgery. These guidelines are based on international health standards to ensure patient safety and effectiveness.
- Body Mass Index (BMI): The procedure is generally recommended for individuals with a BMI of 40 or higher (morbidly obese). It is also an option for those with a BMI between 35 and 40 who are also suffering from obesity-related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea.
- Age Limit: The established age range for this surgery is typically between 18 and 65. Patients must have completed their physical development, and a doctor's special approval may be required for individuals over 65 due to the decreased performance of organs with age.
- Exclusion Criteria: Gastric sleeve surgery is not performed on individuals with active eating disorders, those who are pregnant, or those whose organ development is not yet complete.
The Surgical Procedure
Gastric sleeve surgery is performed using a minimally invasive technique that offers significant advantages.
- Method: The operation is performed laparoscopically, which means the surgeon makes several tiny incisions (around 0.5 cm) in the abdomen rather than one large one. A small camera is inserted through one incision, allowing the surgeon to view the stomach on a monitor while performing the surgery with specialized instruments.
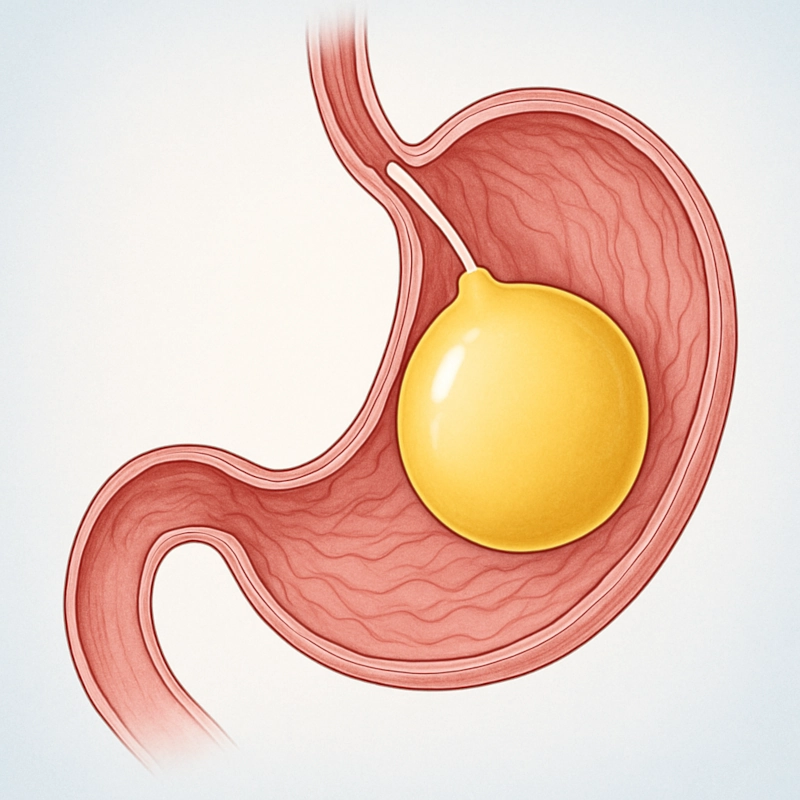
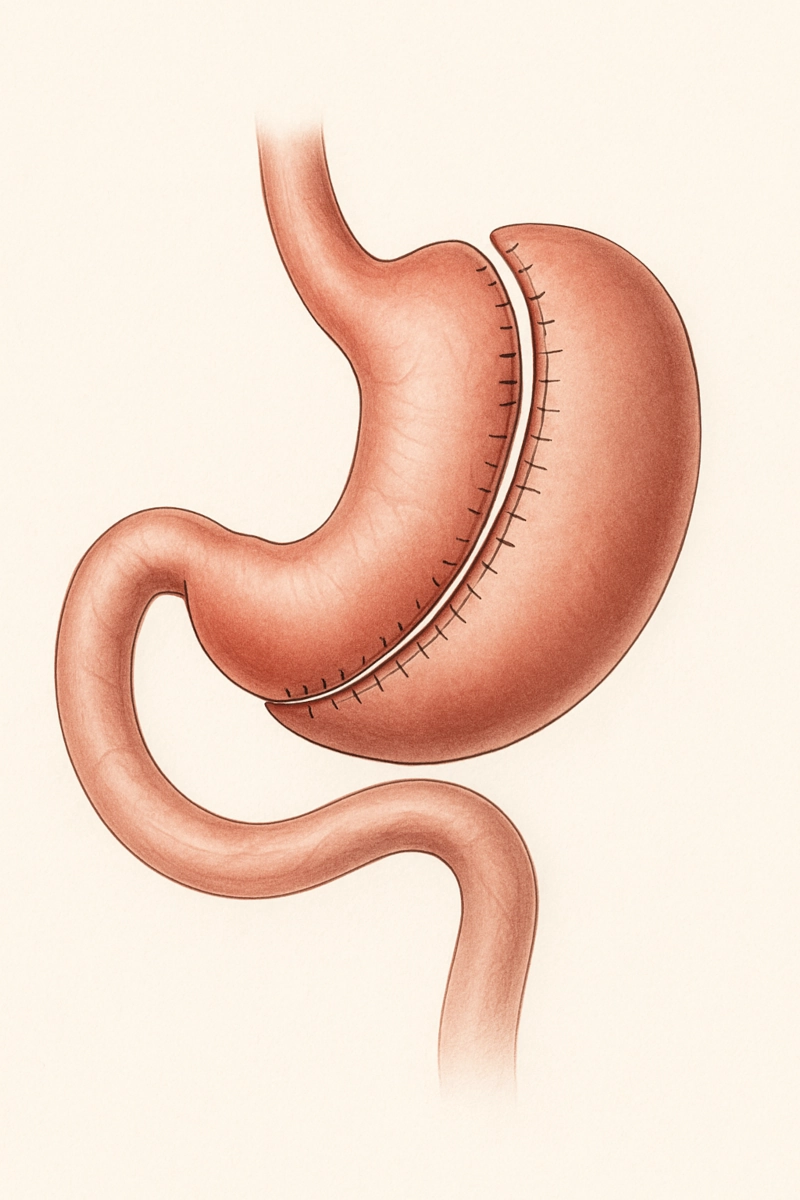
- Process: During the procedure, the surgeon removes approximately 80% of the stomach, particularly the stretched and more deformable part. This leaves behind a much smaller, tube-shaped stomach or "sleeve." This new stomach structure restricts the amount of food that can be consumed. It also affects gut hormones, particularly the satiety hormone, helping the person feel full sooner.
- Final Checks: After the stomach is re-sized and sutured, the surgeon performs a leak test, often by inflating the new stomach with a special dye, to ensure there is no bleeding or leakage from the incision line.
- Duration: The entire surgical process takes approximately 1.5 to 2 hours. Factoring in the time to administer and recover from general anesthesia, the patient is typically in the operating and recovery rooms for a total of 3-4 hours.
Preparing for Your Surgery
Before the operation, patients must follow several steps to prepare their bodies and ensure the best possible outcome.
- Pre-Operative Diet: Patients may be asked to follow a specific diet for about 10 days before surgery. This helps prepare the body for the procedure, often by reducing fat in and around the liver.
- Medical Tests: While initial blood tests provide valuable information, further diagnostics are required. These may include an ECG, chest X-ray, and abdominal ultrasounds to ensure the patient is fit for surgery.
- Stop Smoking: Smoking negatively affects healing and cell renewal. Patients must stop smoking for a period determined by their doctor before the operation.
Life After Gastric Sleeve: Recovery and Lifestyle
A successful outcome depends heavily on post-operative care and long-term lifestyle changes.
- Immediate Recovery: Patients typically stay in the hospital for two nights for monitoring. Light walking is encouraged soon after the surgery to reduce post-operative effects. Sexual intercourse should be avoided for at least two weeks.
- Sleeping Position: To avoid putting pressure on the abdominal incisions, it is recommended to sleep on your right or left side for the first 15 days. After that, sleeping on your back is appropriate. Sleeping in a prone (face-down) position should wait until about one month after surgery.
- Post-Operative Diet: Diet is a critical component of recovery. In the first week, solid foods must be chewed thoroughly or consumed in a pureed form. Adequate protein intake is essential for healing. To avoid stretching the new stomach, solid foods and liquids should not be consumed at the same time; wait at least 45 minutes after eating a solid meal before drinking fluids. Certain foods, like acidic fruits (oranges, grapefruit), high-fiber foods (celery, corn), rice, and bakery products, should be avoided for a period specified by the doctor to prevent discomfort.
Addressing Common Concerns:
Skin Sagging: Rapid loss of subcutaneous fat during weight loss can lead to a loss of skin elasticity and sagging. Using lotions and regular exercise after recovery can help minimize this. In cases of significant sagging, body contouring or stretching surgeries can be performed after the weight loss process is complete. Weight Regain: While significant weight loss is expected for up to 18 months, it is crucial to understand that the stomach can expand again over time. It is not possible to gain weight in the initial months, but if a person reverts to pre-surgery eating habits, weight regain is likely in the long term. Adopting a permanent healthy eating pattern is key to maintaining the results.
Risks and Side Effects
Like any major surgery, gastric sleeve has potential risks and side effects, which can be divided into two categories.
Surgical Risks:
- Excessive bleeding or blood clots
- Infection
- Leakages in the gastrointestinal tract
- Lung or respiratory problems
- Ulcer or acid reflux
- Dumping syndrome (food moves from stomach to small bowel too quickly)
- In rare cases, death.
Dietary Risks:
- Nutrient deficiencies due to limited food intake.
- Irregularities in bowel function.
Cost of Gastric Sleeve Surgery
The price of gastric sleeve surgery is determined by various factors. Since the procedure is often performed to resolve serious health problems, the total cost can include treatments for these associated conditions. A final price cannot be determined without a preliminary examination and consultation with a doctor, who will assess the patient's specific needs.