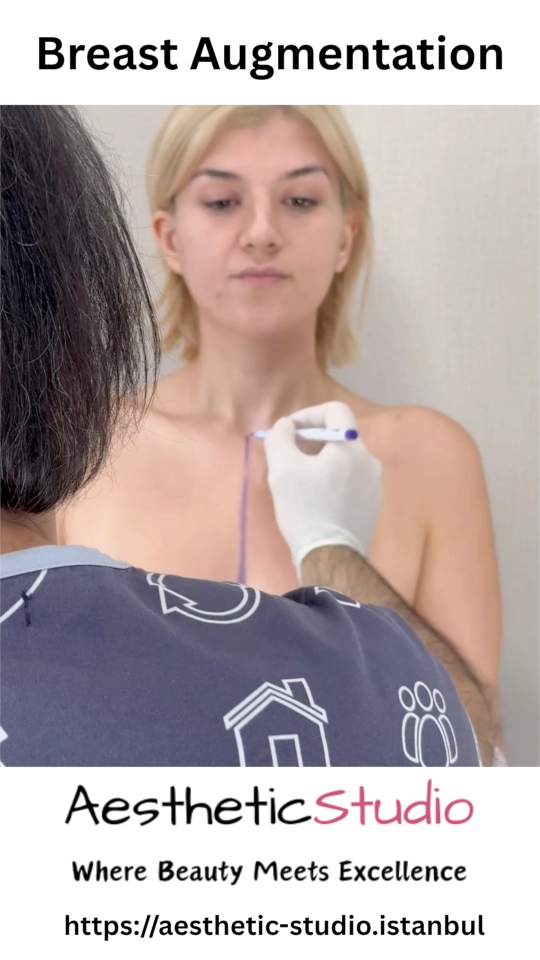
Breast Augmentation
Category: Breast
Treatment Details
Session
1
Operation length
1-3 hours
Anesthesia
General
Discomfort Period
3-7 Days
Return to work
3-7 days
Full Recovery
Should be checked
Results
Permanent
Hospital Stay
1 Day
What is Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation, medically known as augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure to increase the size, improve the shape, and enhance the fullness of the breasts. It is one of a patient's most personal and transformative cosmetic procedures, often referred to as a "breast aug" or "boob job." Women choose to undergo this procedure for a variety of reasons. Some seek it for aesthetic purposes to achieve what they feel is a more ideal physique, improve body symmetry, and boost their self-image and confidence. Others opt for augmentation to reconstruct the breast after a mastectomy or injury, or to restore breast volume that may have been lost after pregnancy, weight loss, or breastfeeding. This enhancement is typically achieved in one of two ways: by surgically placing breast implants or through fat transfer, where fat from another part of the patient's body is used to augment the breasts.
Breast Augmentation vs. Breast Lift: Understanding the Difference
It is crucial to understand what breast augmentation can and cannot do. This procedure is designed to increase volume and improve projection. It does not correct severely drooping or sagging breasts. For breasts that are sagging, a breast lift (mastopexy) is the required procedure to raise the breast and nipple to a more youthful position. In many cases, patients desire both increased volume and a lift. In this situation, a surgeon can perform a breast augmentation and a breast lift at the same time. An experienced plastic surgeon can help you decide which procedure or combination of procedures will best meet your goals.
Who is a Good Candidate for Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation is a highly personal procedure that should be done for oneself, not for others. For this reason, personal satisfaction and realistic expectations are key to a successful outcome. You may be an ideal candidate for breast augmentation if:
- You are physically healthy with no underlying diseases that could impair healing.
- You are not pregnant or currently breastfeeding.
- Your breasts are fully developed.
- You feel your breasts are naturally too small for your body frame.
- You are discontented with the loss of shape or volume after pregnancy, weight loss, or aging.
- You notice that one breast is smaller than the other, causing asymmetry.
- The upper part of your breast appears "empty" or deflated.
Types of Breast Implants
There is a wide variety of breast implants available, and the best choice depends on the patient's anatomy, desired look, and surgeon's recommendation. The main types include:
- Saline Breast Implants: A silicone shell filled with sterile salt water.
- Silicone Breast Implants: A silicone shell filled with a soft, cohesive silicone gel.
- Structured Implants: A saline-filled implant with an inner structure that helps it feel more like a silicone implant.
- "Gummy Bear" Implants: A form-stable implant made of highly cohesive silicone gel that holds its shape.
- Implant Shapes: Implants come in round or teardrop (anatomical) shapes.
- Implant Surfaces: Implants can have a smooth or textured outer shell.
The Surgical Procedure
Anesthesia The procedure typically begins with the administration of anesthesia. While some cases may be done with local anesthesia (where you are awake but the chest area is numb), most patients receive general anesthesia to be comfortably asleep during the surgery. Incision Options The surgeon makes an incision to create a pocket for the implant. There are several common incision locations:
Inframammary: In the natural crease underneath the breast.
Periareolar: Around the edge of the areola.
Transaxillary: In the underside of the armpit. An endoscope (a small camera) is then used to place the implant. This method avoids a scar on the breast itself. Implant Placement The implant can be placed in two main positions:
Submuscular: Underneath the pectoral muscle.
Subglandular (or Submammary): Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle. Closing the Incisions The incisions are closed with layered sutures, skin adhesive, or surgical tape. Over time, these incision lines will fade. The final quality of the scar depends on genetics and proper post-operative care.
Preparing for Your Surgery
Before the procedure, your surgeon will provide you with specific instructions, which may include:
- Getting a blood test or medical evaluation.
- Reviewing your current medications and medical history.
- Stopping smoking and limiting alcohol use.
- Avoiding anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen, which can increase bleeding.
- Ensure your procedure is performed in an accredited hospital or outpatient surgical facility by a board-certified plastic surgeon.
What to Expect After Surgery
After the procedure is complete, you will be taken to a recovery room for monitoring.
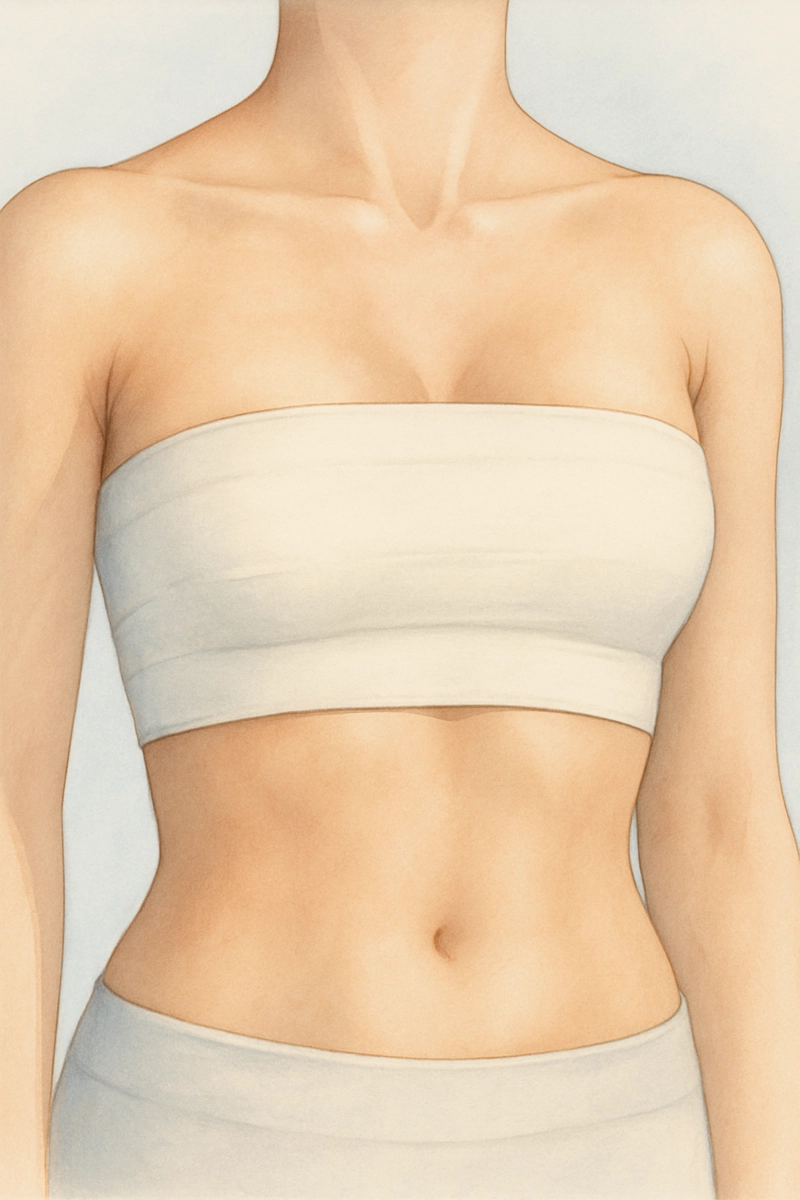
- Dressings: Your breasts will be wrapped in gauze and an elastic bandage or a supportive sports bra to minimize swelling and support the breasts as they heal.
- Medication: Your physician will prescribe pain medication to manage discomfort and may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Recovery at Home: You will typically be allowed to leave the facility once you are stable, usually after one to two hours. You must wear the recommended support garments around the clock for the period your doctor suggests. It is normal to experience some soreness and swelling for a few weeks, with the most significant pain subsiding after two to five days. Avoid strenuous activities until your plastic surgeon gives you clearance.